
Honeybee Robotics Ships Phobos Mining System to JAXA
Honeybee Robotics has partnered with NASA and the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to study the Martian moons, Phobos and Deimos. Honeybee Robotics designed and fabricated a Pneumatic Sampler, or P-Sampler, that will capture surface material on Phobos.
The Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission, led by JAXA, sets out to observe processes in the circumplanetary environment of Mars and determine the origin of Phobos and Deimos. To accomplish this, JAXA will use remote sensing, in-situ observations, and laboratory analyses of the returned samples collected by the coring sampler (C-Sampler) and P-Sampler.
The P-Sampler is mounted along the leg of the MMX lander and will perform sampling operations as soon as 5 seconds after landing on Phobos and up to 3 seconds before liftoff. To collect regolith, high-pressure nitrogen gas is used to excavate and loft surface material. The gas acts as a sweeping agent to move surface material into a sample return canister. Since no mechanisms or motors are involved in the P-Sampler’s collection process, the sampling architecture is fast, robust, and cost-efficient. Using ultra-pure nitrogen gas also reduces the risk of contamination. To date, Honeybee Robotics has conducted hundreds of tests to characterize the performance of the P-Sampler.
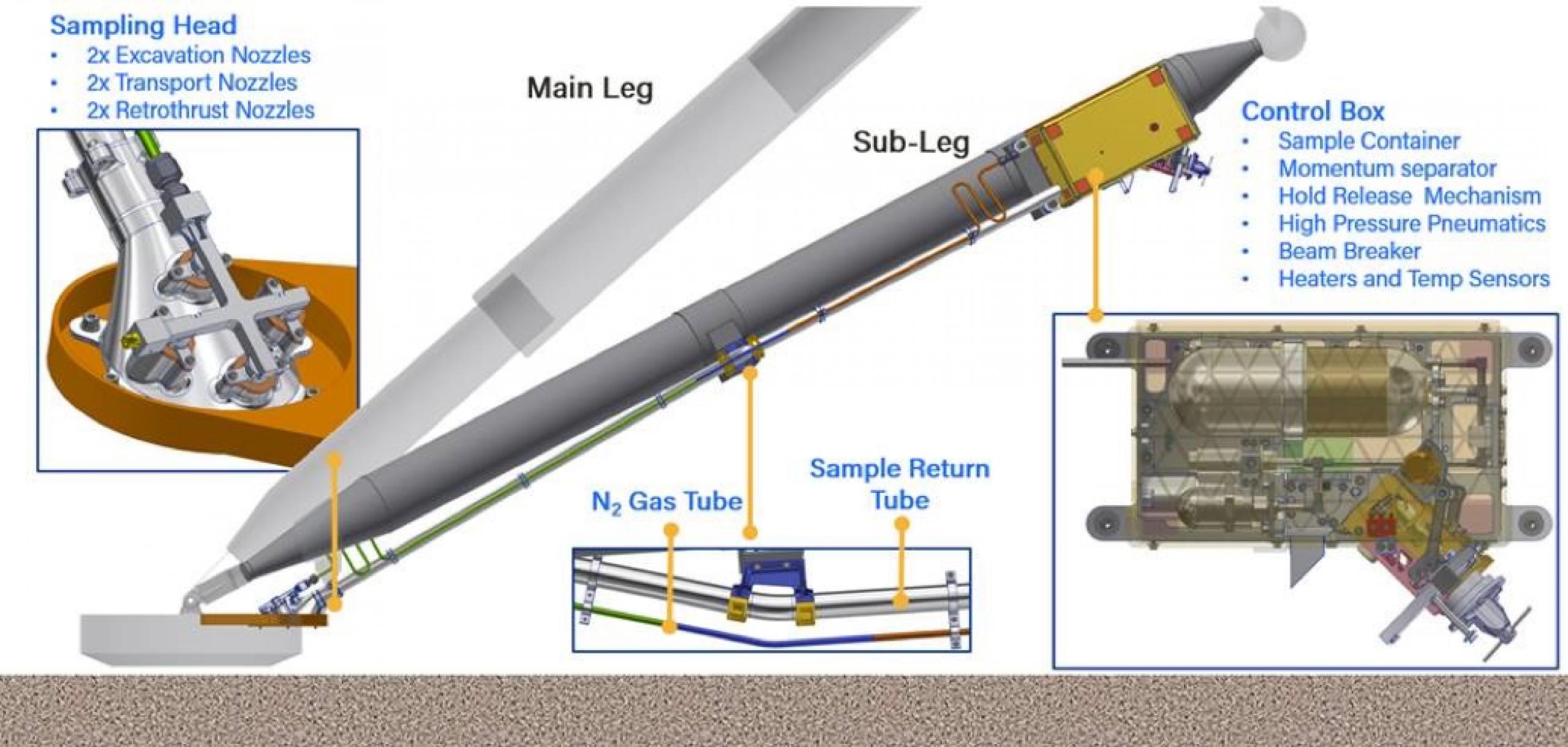
P-Sampler is a derivative of Honeybee Robotics’ PlanetVac technology developed under NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program and matured via funding from NASA’s TechFlights program and the Planetary Society. Recently, Honeybee also produced the Lunar PlanetVac, another iteration of our pneumatic sampling systems, for NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program. Lunar PlanetVac will be on board FireFly’s Blue Ghost Lunar Lander when it launches in mid-2024 to Mare Crisium. As Kris Zacny, Vice President of Exploration Systems at Honeybee Robotics, says, “PlanetVac seeks to greatly simplify the way we collect samples on other worlds. We designed the system to be flexible for a wide variety of applications, and we’re already demonstrating that by flying it on two very different missions to two different moons in the Solar System.”
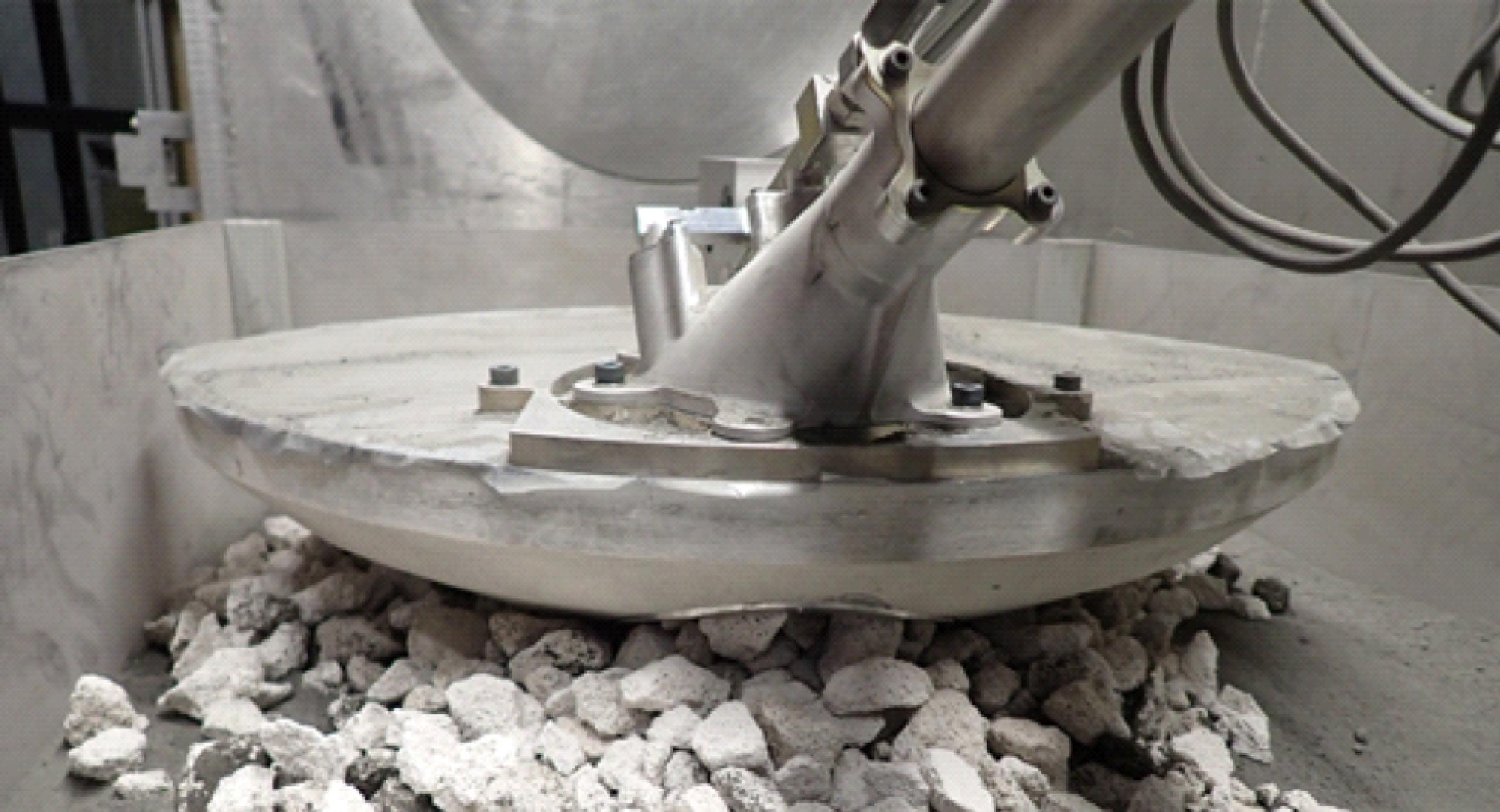
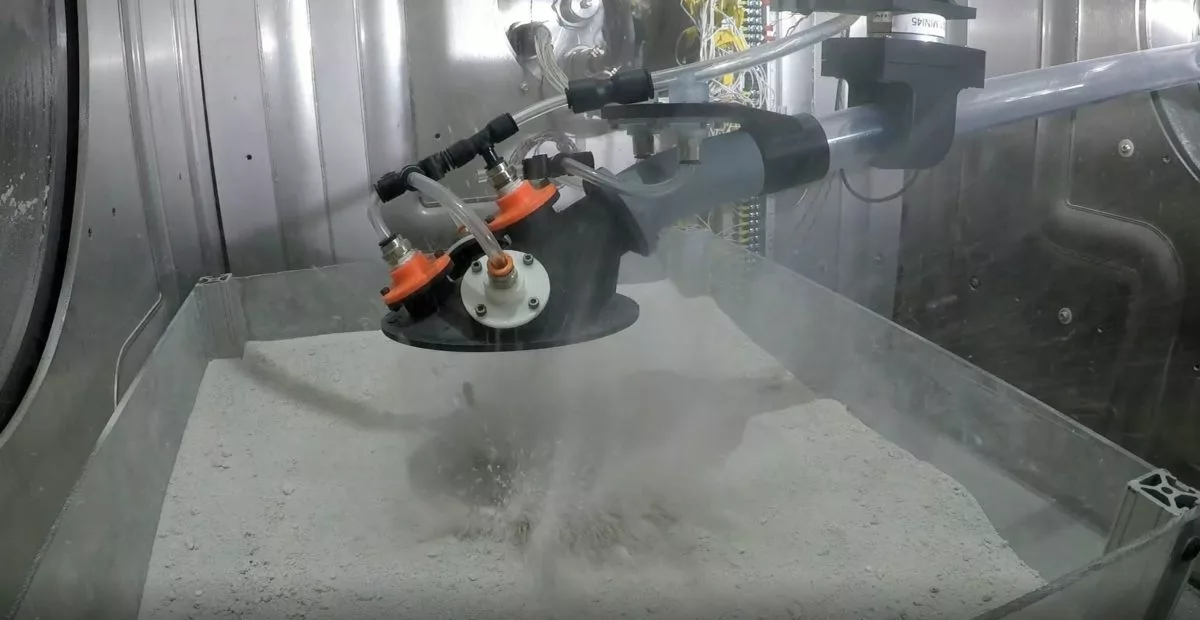


Honeybee Robotics completed testing and shipped the P-Sampler to JAXA in February 2023. Japan’s MMX spacecraft, which will carry the pneumatic sampling system, is scheduled to launch in 2024 and return samples from Phobos in 2029. MMX is making history as the first sample return mission of any Mars-related material.
Read More:
https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20210013273/downloads/ASCEND-Abstract-MMX_4April2021.pdf
